The Principle of Conservation
of Linear Momentum
The law of momentum conservation can be
stated as follows:
For a collision occurring between object
1 and object 2 in an isolated system, the total
momentum of the two
objects before the
collision is equal to the total momentum
of the two objects after
the collision.
That is, the momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by
object 2.
An isolated system is a
system which is free from the influence of a net external force.
The above statement tells us
that the total momentum of a collection of objects (a system) is
conserved" - that is the total amount of momentum is a constant.
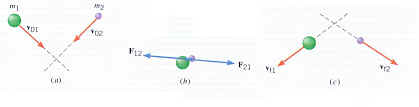

Object 1:
(W1
+ F12)
/\t = m1 Vf1 - m1 V01
External force + Internal
force
Object 2:
(W2
+ F21)
/\t = m2 Vf2 - m2 V02
External force +
Internal force





